Why Use a Data Warehouse?
Scenario 1 - Reporting:
- ABC Pvt Ltd is a company with branches at Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai and Bangalore.
- The Sales Manager wants quarterly sales report.
- Each branch has a separate operational system.
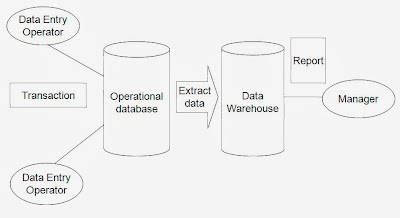
- Extract sales information from each database.
- Store the information in a common repository at a single site.
- Generate automated reports for each branch
- One Stop Shopping Super Market has huge operational database.
- Whenever Executives wants some report the OLTP system becomes slow and data entry operators have to wait for some time.
- Extract data needed for analysis from operational database.
- Store it in warehouse.
- Refresh warehouse at regular interval so that it contains up to date information for analysis.
- Warehouse will contain data with historical perspective.
- Create dashboards for Executives.
- Cakes & Cookies is a small,new company.President of the company wants his company should grow.He needs information so that he can make correct decisions.
Solution 3 - Analytics:
- Improve the quality of data before loading it into the warehouse.
- Perform data cleaning and transformation before loading the data.
- Use query analysis tools to support adhoc queries and decision-making.
What is a Data Warehouse?
Bill Inmon's Definition:
A data warehouse is
- Subject-oriented
- Integrated
- Time-variant
- Non-volatile
Subject-oriented means?
- Data warehouse is organized around subjects such as sales,product,customer.
- It focuses on modeling and analysis of data for decision makers.
- Excludes data not useful in decision support process.

Integration means?
- Data Warehouse is constructed by integrating multiple heterogeneous sources.
- Data Pre-processing are applied to ensure consistency.
- In terms of data.
- Encoding structures.
- Measurement of attributes
- Physical attribute of Data
- Naming conventions.
- Data type format
Time Variant means?
- Provides information from historical perspective e.g. past 5-10 years
- Every key structure contains either implicitly or explicitly an element of time.
Non Volatile means?
- Data once recorded cannot be updated.
- Data warehouse requires two operations in data accessing.
- Initial loading of data
- Access of data
- Data Warehouse server
- almost always a relational/dimensional DBMS, rarely flat files
- OLAP servers
- to support and operate on multi-dimensional data structures
- Clients
- Query and reporting tools
- Analysis tools
- Data mining tools.
- Star Schema.
- Fact Constellation Schema.
- Snowflake Schema.
Star Schema
- A single, large and central fact table and one table for each dimension.
- Every fact points to one tuple in each of the dimensions and has additional attributes.
- Does not capture hierarchies directly.
Snow Flake Schema
- Variant of star schema model.
- A single, large and central fact table and one or more tables for each dimension.
- Dimension tables are normalized i.e. split dimension table data into additional tables.
Fact
Constellation
- Multiple fact tables share dimension tables.
- This schema is viewed as collection of stars hence called galaxy schema or fact constellation.
- Sophisticated application requires such schema.
Building Data Warehouse
- Data Selection
- Data Pre-processing
-Remove inconsistency
- Data Transformation & Integration
- Data Loading
Need for Data Warehouse
- Industry has huge amount of operational data.
- Knowledge worker wants to turn this data into useful information.
- This information is used by them to support strategic decision making .
- It is a platform for consolidated historical data for analysis.
- It stores data of good quality so that knowledge worker can make correct decisions.
- From business perspective
- it is latest marketing weapon
- helps to keep customers by learning more about their needs .
- valuable tool in today’s competitive fast evolving world.










No comments:
Post a Comment